Vitamin As are a group of compounds responsible for cell and tissue growth and differentiation, maintaining the reproductive system, formation of bones and teeth, acting as a powerful antioxidant, strengthening the immune system, building healthy skin and mucous linings, supporting healthy hair and nails, promotes healthy skin aging and it may help prevent skin conditions including acne. Sources include liver, butter, sweet potato, carrots, leafy greens, squash, pumpkin, cheese, cantaloupe, bell pepper, and eggs.
Quick Facts
-A group of similar compounds called retinoids, including retinol, retinal, and retinoic acid
-Responsible for cell and tissue growth and differentiation
-Maintains strong eyes and eyesight, protects against cataracts, helps prevent macular degeneration, helps maintain the reproductive system, important for formation of bones and teeth, a powerful antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals helping to prevent cancers and cardiovascular disease, strengthens the immune system, builds healthy skin and mucous linings that also help protect against infection, supports healthy hair and nails, may help prevent skin conditions including acne, promotes healthy skin aging [160]
-Not water soluble
-Retinol is the form of vitamin A that comes from animal foods, and it is a precursor to the most potent form of vitamin A in the body: retinoic acid
-Beta-carotine is the form of vitamin A from plant foods, which can be converted into retinol in the body
-Beta-carotine converts to retinol in different efficiencies depending on the type. -Beta-carotine from supplements converts to retinol at a 2:1 ratio, and beta-carotine from food converts at a 12:1 ratio. This means animal foods are a more efficient source of vitamin A.
[43][44]
RDI
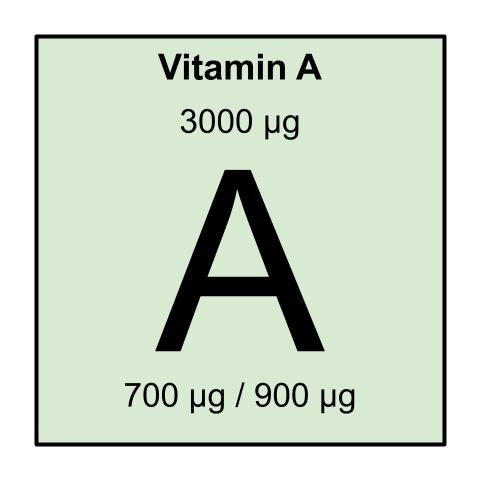
Males 19 – 30 yrs: 900 μg
Females 19 – 30 yrs: 700 μg
[128]
Deficiency
-Poor teeth formation, slow bone formation, night blindness. Prolonged deficiency may cause dry eyes and eventually blindness, rough dry scaly skin, bumpy skin, more likely to get colds and viral infections, chronic inflammation on the sinuses (sinusitis), frequent bladder or urinary tract infection, more likely to get ear abscesses, rapid weight loss, loss of smell, loss of taste, loss of appetite [160]
Toxicity
-Headache and rash
-Increased intracranial pressure, drowsiness, irritabilit, abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, sometimes skin peeling
-Early symptoms: coarse hair, alopecia of the eyebrows, dry, rough skin, dry eyes, cracked lips. [162]
-An upper limit of 3,000 μg is recommended [https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/VitaminA-HealthProfessional/]
Sources
Liver, butter, sweet potato, carrots, leafy greens, squash, pumpkin, cheese, cantaloupe, bell pepper, egg [43][44]
*Bioavailability increases when consumed with fats