Sulphur is involved in protein synthesis, many enzyme reactions, and the production of collagen. It is a part of some amino acids, and part of keratin, which gives strength to hair, nails, and skin. It is the third most abundant mineral in the body. Sources include protein rich animal foods like meat, egg, poultry, dairy, and seafood as well as onions, garlic, leafy dark green vegetables.
Quick Facts
-Third most abundant mineral in the body [129]
-Part of some amino acids, and part of keratin, which gives strength to hair, nails, and skin
-Involved in protein synthesis, many enzyme reactions, the production of collagen
[80]
RDI
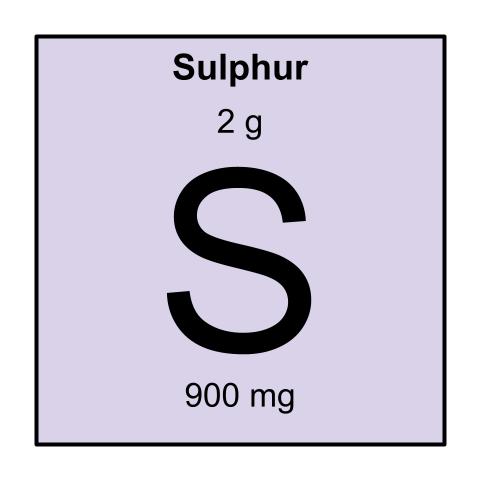
800 – 900 mg / day [203]
Sulfur needs are met almost exclusively through protein since certain amino acids contain sulphur, so RDI is linked to protein intake [129].
Deficiency
-Rare, however some scientists believe that it is becoming a larger issue as we eat more processed foods devoid of sulphur and that this contributes to increasing rates of obesity, chronic fatigue, heart disease, skin problems, allergies and Alzheimer’s [204][205].
Toxicity
-Most people cannot overdose on sulphur because excess is excreted through urine
-Symptoms are minor and may include diarrhea and flatulence in the case of overdose
-If supplementing, take no more than 2 grams per day. The amount of grams of the supplement you take depends on the form [205].
Sources
Protein rich animal foods like meat, egg, poultry, dairy, and seafood [80] Onions, garlic, leafy dark green vegetables [206]