Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals and delays degenerative diseases, decreases risk of prostate and bladder cancer, slows oxidation, which reduces cellular aging, increases functioning of the immune system, in combination with Vitamin A it protects the lungs from pollution, helps protect the skin from sun damage, lowers risk of skin cancer, may reduce risk of cataracts or age related macular degeneration, may help prevent neurological decline and disease like Alzheimer’s, helps lower blood pressure and protects against atherosclerosis and heart disease, important for red blood cell formation. Sources include sunflower seeds, almonds, hazelnuts, cold pressed vegetable oils, dark green leafy vegetables, avocados, blueberries, brown rice, dried beans, and egg yolk. It is also commonly added to preserved foods.
Quick Facts
-A group of 8 fat soluble compounds including 4 Tocopherols and 4 Tocotrienols
-Mainly functions as an antioxidant protecting cell membranes from reactive oxygen species
-Affects genetic expression, and is an enzyme activity regulator
-Not water soluble [59]
-Antioxidant that neutralizes free radicals and delays degenerative diseases, decreases risk of prostate and bladder cancer, slows oxidation, which reduces cellular aging, increases functioning of immune system, in combination with Vitamin A, it protects the lungs from pollution, helps protect the skin from sun damage, lowers risk of skin cancer, may reduce risk of cataracts or age related macular degeneration, may help prevent neurological decline and disease like Alzheimer’s, helps lower blood pressure and protects against atherosclerosis and heart disease, important for red blood cell formation [160]
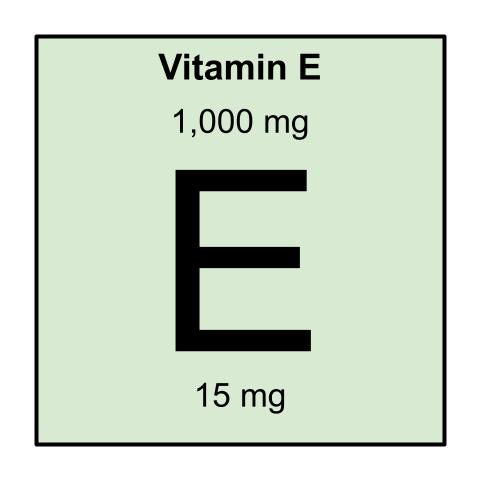
RDI
Males 19 – 30 yrs: 15 mg
Females 19 – 30 yrs: 15 mg
[128]
Deficiency
-Loss of appetite, nausea, anemia from loss of red blood cells, weak immune system, eye problems like cataracts and degeneration of retina, angina (severe chest pain) in males, weak muscles and limbs, muscle cramps, stiffness or spasms, nerve damage characterized by numbness, tingling, or burning sensation in arms, legs, hands, or feet, lack of muscle coordination – jerkiness, clumsiness, instability, digestive problems including liver and gallbladder disorders – results in poor digestion of nutrients, miscarriages, uterine or testicular deterioration, decreased fertility [160]
Toxicity
-Doses of 400 – 800 mg/day don’t show side effects over months or years
-An upper limit of 1000 mg/day is recommended. Sometimes, muscle weakness, fatigue, nausea, and diarrhea occur. Bleeding may occur in doses higher than 1000 mg/day [177]
Sources
Wheat germ oil, sunflower seeds, almonds, hazelnuts. Also commonly added to preserve foods.
[59], cold pressed vegetable oils like sunflower, soybean, and safflower, dark green leafy vegetables like swiss chard, mustard greens, spinach, and turnip greens. Also avocados, blueberries, brown rice, dried beans, egg yolk, kiwi, legumes, nuts and seeds, oatmeal, organ meats, olives, papaya, soybeans [160]
*Bioavailability increases when consumed with fats